
- #CENTOS 7 STATIC IP HOW TO#
- #CENTOS 7 STATIC IP DRIVER#
- #CENTOS 7 STATIC IP WINDOWS#
Restart back to normal mode before installing the printer again. If you want to have multiple IP addresses by creating an alias for eth0:0, create the following file: vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0:0 IP Aliasing DEVICE'eth0:0' BOOTPROTO'static' HWADDR20:89:84:c8:12:8a NMCONTROLLED'no' ONBOOT'yes' TYPE'Ethernet' IPADDR192.168.0.109 NETMASK255.255.255.0 GATEWAY192.168.0.1 DNS18.8.8.8 DNS18.8.4.
#CENTOS 7 STATIC IP WINDOWS#
Use Windows diagnostic mode to troubleshoot issues with Autodesk software).
#CENTOS 7 STATIC IP DRIVER#
If the driver still will not remove, restart the computer in a diagnostic startup and then use the printui /s /t2 command to remove the driver package(s) (see If a message appears about access denied or the printer being in use and the driver or any installed program is not found that would account for this, restart the computer. Windows XP does not have this extra choice. Note: Removing the driver package will clear all driver installation files for that device, leaving no reference to the printer that Windows could possibly use to auto-reinstall again.
Select "Remove driver and driver package" and click OK. Select the printer driver to uninstall. Click the File menu and choose "Server Properties.". There are two ways we can assign a static IP address in CentOS 8 systems, 1- Using Network manager. #CENTOS 7 STATIC IP HOW TO#
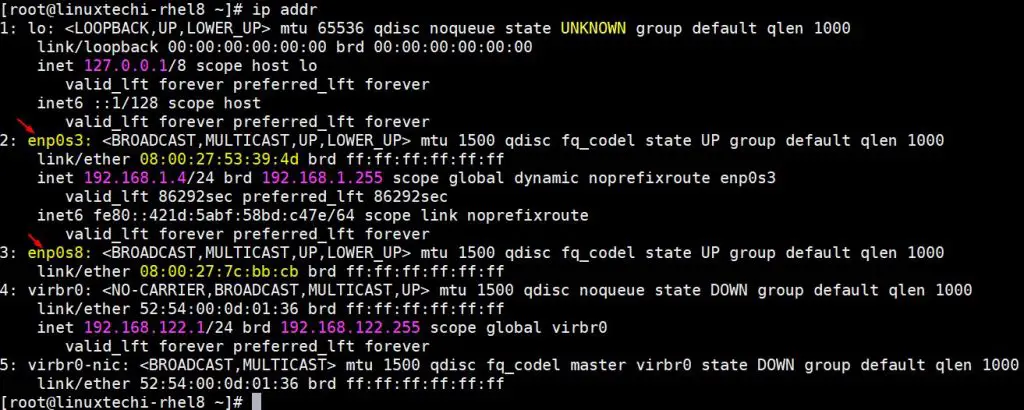
Click Start > Control Panel > Printers and Faxes. In this tutorial, we will learn how to assign static IP addresses in CentOS 7 or 8 machines. 1-First, by entering the following command, we check the status of the network card.After entering the following command, you will be informed whether your network card is active or inactive.
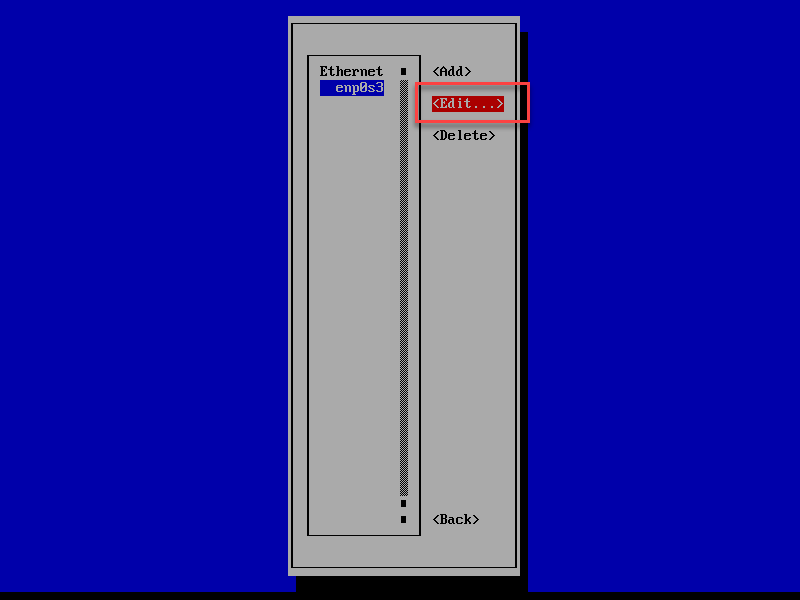 Select any printer and then click "Print server properties" at the top of the window. From the Start menu or the Start screen:. Press the WINDOWS key on the keyboard to display the Start screen, type in printui /s /t2 and then click it in the search list. Press WINDOWS-R on the keyboard to bring up the Run window, type in printui /s /t2 and then press Enter or click OK. Click the Start menu and in the search field type printui /s /t2 and then press Enter or click it in the search list. Open the Print Server Properties dialog window by doing one of the following:. To completely remove printer driver files from a system: To view or setup a static IP using this tool for eth0, enter:įig.04: nmtui is a curses?based TUI application for interacting with NetworkManager.Not doing these before attempting to remove the driver files may result in an "access denied" or "printer in use" error. To show a connection editor that supports adding, modifying, viewing and deleting connections. It is a curses?based TUI application for interacting with NetworkManager. To restart networking service, enter:įig.03: Testing networking and make sure everything is working How do I configure an eth0 interface with static IP address on CentOS 7 / RHEL 7 using Network Manager (method # 2)? You do not need to specify the network or broadcast address as this is calculated automatically by the system. # This is system specific and can be created using 'uuidgen eth0' command # Update/edit as follows for static IP configuration: # static IP address on CentOS 7 or RHEL 7# Let us configure our system for the following information. Configure Static IP Address in CentOS 7 / RHEL 7. But, if you go to the bigger organizations, they use static (manual) IP to avoid network issues due non-availability of DHCP servers. # vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 READ: How To configure DHCP server on CentOS 7, Ubuntu 18.04 & Debian 9. To configure an eth0 interface with static network settings using ifcfg files, edit or create a file with name ifcfg-eth0 in the /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ directory as follows: NAME="eth0" How do I configure an eth0 interface with static network IP settings (method # 1)? Fig.01: List NICs in a CentOS 7 server using ip commandOr use the following command:įig.02: nmcli command in actionHere is a typical DHCP configration for eth0 (stored in /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 file): DEVICE="eth0"
Select any printer and then click "Print server properties" at the top of the window. From the Start menu or the Start screen:. Press the WINDOWS key on the keyboard to display the Start screen, type in printui /s /t2 and then click it in the search list. Press WINDOWS-R on the keyboard to bring up the Run window, type in printui /s /t2 and then press Enter or click OK. Click the Start menu and in the search field type printui /s /t2 and then press Enter or click it in the search list. Open the Print Server Properties dialog window by doing one of the following:. To completely remove printer driver files from a system: To view or setup a static IP using this tool for eth0, enter:įig.04: nmtui is a curses?based TUI application for interacting with NetworkManager.Not doing these before attempting to remove the driver files may result in an "access denied" or "printer in use" error. To show a connection editor that supports adding, modifying, viewing and deleting connections. It is a curses?based TUI application for interacting with NetworkManager. To restart networking service, enter:įig.03: Testing networking and make sure everything is working How do I configure an eth0 interface with static IP address on CentOS 7 / RHEL 7 using Network Manager (method # 2)? You do not need to specify the network or broadcast address as this is calculated automatically by the system. # This is system specific and can be created using 'uuidgen eth0' command # Update/edit as follows for static IP configuration: # static IP address on CentOS 7 or RHEL 7# Let us configure our system for the following information. Configure Static IP Address in CentOS 7 / RHEL 7. But, if you go to the bigger organizations, they use static (manual) IP to avoid network issues due non-availability of DHCP servers. # vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 READ: How To configure DHCP server on CentOS 7, Ubuntu 18.04 & Debian 9. To configure an eth0 interface with static network settings using ifcfg files, edit or create a file with name ifcfg-eth0 in the /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ directory as follows: NAME="eth0" How do I configure an eth0 interface with static network IP settings (method # 1)? Fig.01: List NICs in a CentOS 7 server using ip commandOr use the following command:įig.02: nmcli command in actionHere is a typical DHCP configration for eth0 (stored in /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 file): DEVICE="eth0"






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
